- Inspire
- Innovate
- Integrate
- Home
- Thermal Imaging – Infrared Thermography
Thermal Imaging – Infrared Thermography
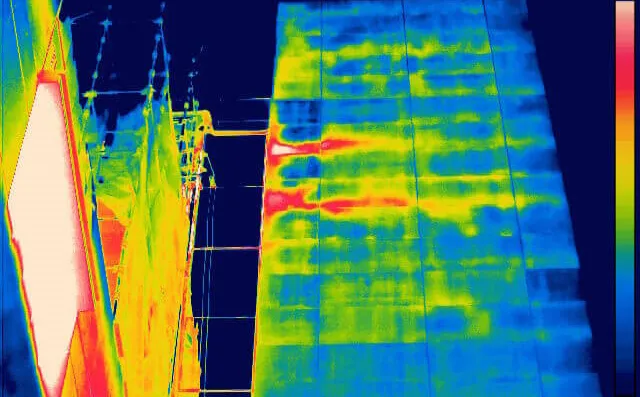
Conserve offers services in Thermal Imaging also known as Infrared Thermography in Qatar. Infrared Thermography detects the surface temperature of exterior surfaces such as facade of buildings, boilers, radiators, electrical panels etc. Infrared thermography uses non-contact method to measure the temperature of surfaces.
Following are the steps in Infrared Thermography study
- Data Collection
- Data Processing and Analysis
- Preparation of report
Data Collection:
By using the IR Cameras we detect the infrared energy i.e heat with the focused Line of sight and then capture the Images. Infrared cameras are available in various resolutions. The appropriate camera has to be selected based on the application. Conserve has wide variety of Infrared Cameras for different applications.
Data Processing and Analysis:
The captured Images are converted into an electronic signal, which is then processed to produce a thermal image on a video monitor. The image basically shows the temperature distribution on the surface. The temperature distribution is shown in different colors from red to blue. Red refers to highest temperature and blue the lowest temperature.


Reports:
An application Engineer should be able to read the temperature distribution shown in the infrared camera and interpret the results. The results are used to find infiltration, air leakage, failure of insulation or nonperformance of insulation etc.
Applications:
- Detection of HVAC System Leakages.
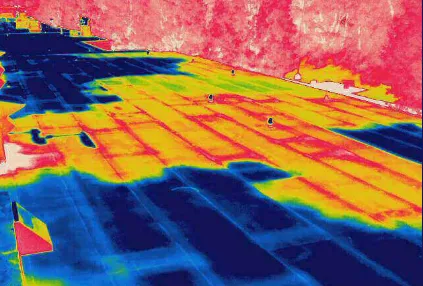
- Detection of Roof Leakages.
- Detection of the Leakages and its Route.
- Detection of Wall Insulations and Calculate energy losses.
- A tool for Energy Audits.
Quick Links
Copyrights © 2026. Conserve Solutions. All Rights Reserved.

